GPT OSS - OpenAI Reference Implementation
Load OpenAI's reference implementation
In this post, we load the gpt oss reference implementations from OpenAI. OpenAI provided 2 different implementations - torch and triton implementations. As we will see, they differ slightly on how MoE layers are quantized.
Architecture
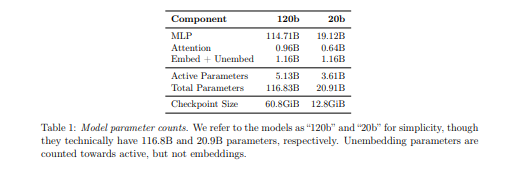
Below we show the architecture of the 20B variant of GPT-OSS model.
Model card
It’s a mixture-of-experts (MoE) model, which improves computational efficiency by routing inputs through specialized expert subnetworks. In addition, this seems to also reveal that OpenAI is using Grouped Query Attention (GQA) for their models (at least based on this open source release), instead of Grouped Head Latent Attention, that is used by DeepSeek V3.
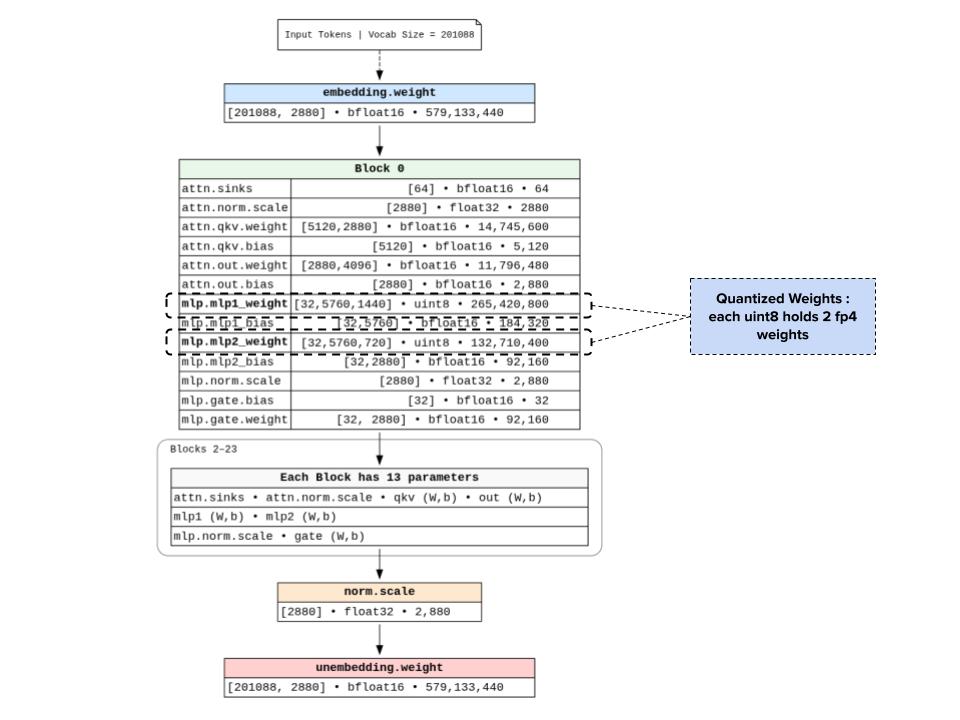
Below is the details of the parameters and how they are distributed across the layers. Majority of the parameters are MLP layers that are in the MoE layers.
We inspected the huggingface version of the model in a previous post
Load torch model
To get started, you will need to install the python package with gpt-oss implementations locally. There are instructions in the gpt-oss repo. Here’s what I did:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# create environment. code only works with python=3.12
conda create -n gpt_oss python=3.12
conda activate gpt_oss
# Download the weights
hf download openai/gpt-oss-20b --include "original/*" --local-dir gpt-oss-20b/
# install triton dependencies
git clone https://github.com/triton-lang/triton
cd triton/
pip install -r python/requirements.txt
pip install -e . --verbose --no-build-isolation
pip install -e python/triton_kernels
# install all gpt-oss packages
git clone org-14957082@github.com:openai/gpt-oss.git
cd gpt-oss
pip install .
Load Model checkpoints
As I mentioned before, there are 2 different versions of the model that are provided.
1
2
from gpt_oss.torch.model import Transformer
from gpt_oss.triton.model import Transformer as TritonTransformer
You should be able to check the downloaded checkpoint
1
2
3
4
5
import os
checkpoint_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "gpt-oss-20b/original")
print(checkpoint_path)
# '/home/ksharma/***********************************************/gpt-oss-20b/original'
Let’s check the model config
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import json
from gpt_oss.torch.model import ModelConfig
import pprint
config_path = os.path.join(checkpoint_path, "config.json")
with open(config_path, "r") as f:
json_config = json.load(f)
config = ModelConfig(**json_config)
pprint.pprint(config)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
ModelConfig(num_hidden_layers=24,
num_experts=32,
experts_per_token=4,
vocab_size=201088,
hidden_size=2880,
intermediate_size=2880,
swiglu_limit=7.0,
head_dim=64,
num_attention_heads=64,
num_key_value_heads=8,
sliding_window=128,
initial_context_length=4096,
rope_theta=150000,
rope_scaling_factor=32.0,
rope_ntk_alpha=1,
rope_ntk_beta=32)
Load the torch version
Let’s first check we have enough via nvidia-smi
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Fri Sep 5 07:22:41 2025
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 535.247.01 Driver Version: 535.247.01 CUDA Version: 12.2 |
|-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|=========================================+======================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 Off | 00000000:01:00.0 On | Off |
| 0% 47C P8 24W / 450W | 578MiB / 24564MiB | 4% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=======================================================================================|
| 0 N/A N/A 2087 G /usr/lib/xorg/Xorg 255MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2312 G /usr/bin/gnome-shell 80MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 3385 G ...seed-version=20250904-180033.822000 67MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 32885 G /usr/share/code/code 158MiB |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Let’s load the model
1
model = Transformer.from_checkpoint(checkpoint_path, "cuda")
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OutOfMemoryError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[6], line 1
----> 1 model = Transformer.from_checkpoint(checkpoint_path, "cuda")
File ~/dev/git/gpt-oss/gpt_oss/torch/model.py:402, in Transformer.from_checkpoint(path, device)
399 json_config = json.load(f)
400 config = ModelConfig(**json_config)
--> 402 model = Transformer(
403 config=config,
404 device=device,
405 )
406 model.eval()
408 # Load weights
File ~/dev/git/gpt-oss/gpt_oss/torch/model.py:369, in Transformer.__init__(self, config, device)
363 super().__init__()
364 self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(
365 config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, device=device, dtype=torch.bfloat16
366 )
367 self.block = torch.nn.ModuleList(
368 [
--> 369 TransformerBlock(config, layer_idx, device)
370 for layer_idx in range(config.num_hidden_layers)
371 ]
...
306 (config.num_experts, config.hidden_size),
(...) 309 )
310 )
OutOfMemoryError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate 508.00 MiB. GPU 0 has a total capacity of 23.64 GiB of which 446.12 MiB is free. Including non-PyTorch memory, this process has 22.58 GiB memory in use. Of the allocated memory 22.05 GiB is allocated by PyTorch, and 94.18 MiB is reserved by PyTorch but unallocated. If reserved but unallocated memory is large try setting PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF=expandable_segments:True to avoid fragmentation. See documentation for Memory Management (https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/cuda.html#environment-variables)
Output is truncated. View as a scrollable element or open in a text editor. Adjust cell output settings...
Unfortunately, this OOMed. Originally, I expected this torch model to be quantized to mxfp4 but that wasn’t the case. Since the weights aren’t quantized, that means we probably need closer to 40g of GPU memory to load the model. Let’s just load it in CPU to inspect weights.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
model = Transformer.from_checkpoint(checkpoint_path, "cpu")
print(model)
num_parameters = 0
parameters_state_dict = model.state_dict()
for key, value in parameters_state_dict.items():
print(key, value.size(), value.dtype, value.numel())
num_parameters += value.numel()
print(f"Number of parameters: {num_parameters}")
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Transformer(
(embedding): Embedding(201088, 2880)
(block): ModuleList(
(0-23): 24 x TransformerBlock(
(attn): AttentionBlock(
(norm): RMSNorm()
(qkv): Linear(in_features=2880, out_features=5120, bias=True)
(out): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=2880, bias=True)
(rope): RotaryEmbedding()
)
(mlp): MLPBlock(
(norm): RMSNorm()
(gate): Linear(in_features=2880, out_features=32, bias=True)
)
)
)
(norm): RMSNorm()
(unembedding): Linear(in_features=2880, out_features=201088, bias=False)
)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
embedding.weight torch.Size([201088, 2880]) torch.bfloat16 579133440
block.0.attn.sinks torch.Size([64]) torch.bfloat16 64
block.0.attn.norm.scale torch.Size([2880]) torch.float32 2880
block.0.attn.qkv.weight torch.Size([5120, 2880]) torch.bfloat16 14745600
block.0.attn.qkv.bias torch.Size([5120]) torch.bfloat16 5120
block.0.attn.out.weight torch.Size([2880, 4096]) torch.bfloat16 11796480
block.0.attn.out.bias torch.Size([2880]) torch.bfloat16 2880
block.0.mlp.mlp1_weight torch.Size([32, 5760, 2880]) torch.bfloat16 530841600
block.0.mlp.mlp1_bias torch.Size([32, 5760]) torch.bfloat16 184320
block.0.mlp.mlp2_weight torch.Size([32, 2880, 2880]) torch.bfloat16 265420800
block.0.mlp.mlp2_bias torch.Size([32, 2880]) torch.bfloat16 92160
block.0.mlp.norm.scale torch.Size([2880]) torch.float32 2880
block.0.mlp.gate.weight torch.Size([32, 2880]) torch.bfloat16 92160
block.0.mlp.gate.bias torch.Size([32]) torch.bfloat16 32
...2-23
norm.scale torch.Size([2880]) torch.float32 2880
unembedding.weight torch.Size([201088, 2880]) torch.bfloat16 579133440
Number of parameters: 20914757184
Load the triton version
1
2
triton_model = TritonTransformer.from_checkpoint(checkpoint_path, device="cuda")
print(triton_model)
We can see now that the model parameters have changed based on the repr itself where gate has a Parameter Dict that holds bias and weights.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
Transformer(
(embedding): Embedding(201088, 2880)
(block): ModuleList(
(0-23): 24 x TransformerBlock(
(attn): AttentionBlock(
(norm): RMSNorm()
(qkv): Linear(in_features=2880, out_features=5120, bias=True)
(out): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=2880, bias=True)
(rope): RotaryEmbedding()
)
(mlp): MLPBlock(
(norm): RMSNorm()
(gate): ParameterDict(
(bias): Parameter containing: [torch.cuda.BFloat16Tensor of size 32 (cuda:0)]
(weight): Parameter containing: [torch.cuda.BFloat16Tensor of size 2880x32 (cuda:0)]
)
)
)
)
(norm): RMSNorm()
(unembedding): Linear(in_features=2880, out_features=201088, bias=False)
)
How much memory that we use up?
Seems like closer to 18GB
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 535.247.01 Driver Version: 535.247.01 CUDA Version: 12.2 |
|-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|=========================================+======================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 Off | 00000000:01:00.0 On | Off |
| 30% 42C P8 25W / 450W | 18423MiB / 24564MiB | 21% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=======================================================================================|
| 0 N/A N/A 2087 G /usr/lib/xorg/Xorg 327MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 2312 G /usr/bin/gnome-shell 109MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 3385 G ...seed-version=20250904-180033.822000 140MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 32885 G /usr/share/code/code 248MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 626115 C ...a/anaconda3/envs/gpt_oss/bin/python 17574MiB |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Now let’s look at the parameters.
1
2
3
4
5
6
num_parameters = 0
parameters_state_dict = triton_model.state_dict()
for key, value in parameters_state_dict.items():
print(key, value.size(), value.dtype, value.numel())
num_parameters += value.numel()
print(f"Number of parameters: {num_parameters}")
Those uint8 tensors aren’t “real” 8-bit integers in the mathematical sense. They’re packing two MXFP4 values into each byte.
Summary / TLDR
We explored GPT-OSS reference implementation:
- Architecture: 20B parameter MoE model with 24 transformer blocks, 32 experts per MoE layer
- Implementations: PyTorch (40GB VRAM) and Triton-optimized with MXFP4 quantization (18GB VRAM)
- Attention: Uses Grouped Query Attention (GQA) instead of Grouped Head Latent Attention
- Parameter Distribution: Majority concentrated in MoE MLP layers
- Hardware Compatibility: Triton version fits on consumer GPUs like RTX 4090